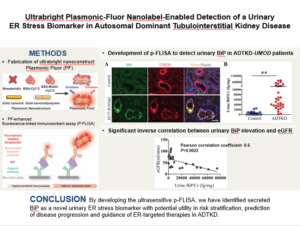
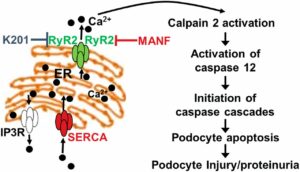
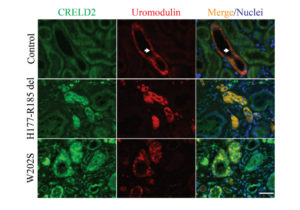
The Division of Nephrology is proud to announce that the American Society for Clinical Investigation (ASCI) has elected Ying Maggie Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, into its 2022 class of members. Founded in 1908, ASCI is one of the oldest and most esteemed nonprofit honor societies of physician-scientists. Dr. Chen is a nephrotic […]
Physician-Scientist Ying Maggie Chen Elected to American Society for Clinical Investigation